In our quest for optimal health, understanding the role of different nutrients can be enlightening. Among these nutrients, carbohydrates often find themselves at the center of dietary discussions. But why are carbohydrates essential for our well-being?
In this article, we’ll explore the various facets of carbohydrates, from their fundamental role in energy production to their impact on mental and physical health. By the end, we’ll appreciate why embracing carbohydrates can be a key to achieving a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Understanding carbohydrates: types and functions
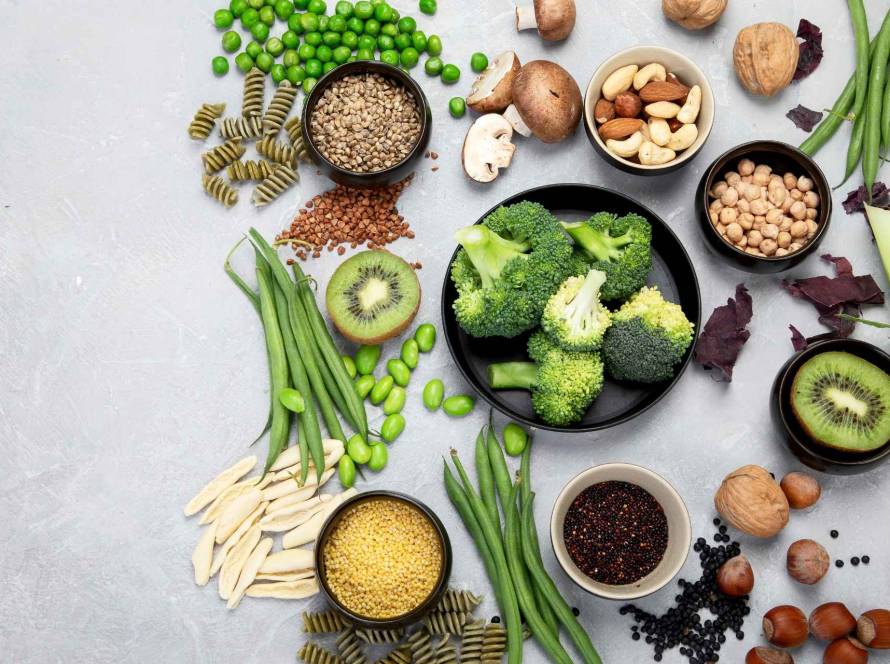
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, typically found in foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes. They are categorized into three main types: sugars, starches and fibers. Each of these plays a unique role in our diet.
- Sugars: these are the simplest form of carbohydrates and include glucose, fructose and sucrose. Sugars are quickly absorbed by the body, providing a rapid source of energy;
- Starches: found in foods like potatoes, rice and bread, starches are complex carbohydrates. They break down into glucose, which serves as a primary energy source for our bodies;
- Fibers: unlike sugars and starches, fibers are not digested by the body. Instead, they aid in digestion and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Understanding these types helps us make informed dietary choices, ensuring we get the right mix of nutrients.
Why are carbohydrates essential for optimal health?
Carbohydrates are not just about energy. They play a pivotal role in maintaining overall health. They support the immune system, promote proper brain function and aid in nutrient absorption.
Energy production
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred energy source. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used by our cells to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy is vital for every bodily function, from the simplest movement to complex mental tasks.
- Immediate energy: studies show that simple carbohydrate ingestion during high-intensity exercise increases blood glucose, enhances performance, and reduces perceived exertion.. This is why athletes often consume energy gels or drinks during competitions;
- Sustained energy: complex carbohydrates, like those found in whole grains, provide a more sustained energy release, which is crucial for endurance activities and maintaining energy levels throughout the day;
- Energy storage: excess glucose is converted into glycogen, stored primarily in the liver and muscles. These glycogen reserves are tapped into during fasting or prolonged exercise. Studies show that increased carbohydrate intake before exercise enhances endurance performance by increasing muscle glycogen levels and delay fatigue.
Without carbohydrates, our bodies would struggle to maintain energy levels, leading to fatigue and decreased performance.
Immune support
Some carbohydrates, especially those found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains, play a key role in supporting immune health by aiding the production and function of immune cells. Immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages rely on glucose as their primary fuel. Without adequate carbohydrate intake, these cells can struggle to respond effectively to infections. Studies show that athletes experience fewer immune disruptions when they consume carbs during prolonged exercise.
Fiber, a type of carbohydrate found in plant foods, feeds gut bacteria. These bacteria ferment fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAS), such as butyrate and propionate. SCFAS play a key role in:
- Strengthening the gut barrier;
- Regulating immune cells;
- Reducing harmful inflammation.
Animal and human studies show a prebiotic-rich diet supports t-regulatory cells and helps balance immune responses.
Brain health
The brain relies heavily on glucose, a carbohydrate-derived sugar, for energy. Without enough dietary carbs, brain function, mood and focus can suffer, while optimal carb intake supports cognition and mental resilience.
According to research, the brain consumes around 20% of our body’s energy, almost exclusively from glucose. A study comparing low-carb and balanced diets found participants on very low-carb regimens performed worse in memory-based tasks, though performance improved after reintroducing carbs.
Nutrient absorption
Carbohydrates facilitate the absorption of essential nutrients.
- Dietary fiber reaches the colon undigested and is fermented by gut microbes, producing SCFAS like butyrate, propionate and acetate, that support the growth of beneficial bacteria and strengthen the gut barrier, creating an environment that improves nutrient absorption and protects against inflammation;
- Soluble fibers, such as inulin, have been shown to improve the absorption of minerals like calcium and magnesium by creating favorable conditions in the colon, according to research;
- Viscous fibers form gels in the gut that slow digestion and smooth out nutrient release. This steady flow allows for more efficient absorption of vitamins, minerals and glucose, avoiding nutrient overload or sudden spikes;
- Insoluble fibers add bulk to stool and improve regular bowel movements. Optimal transit time means nutrients, especially fat-soluble vitamins, have adequate time for absorption along the gut.
Physical performance
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, carbohydrates are a crucial component of their dietary regimen. They enhance performance by replenishing glycogen stores, which are depleted during intense physical activity.
- Pre-workout fuel: a carbohydrate-rich meal before exercise can improve endurance and delay fatigue, allowing athletes to perform at their peak for longer periods;
- Recovery and repair: consuming carbohydrates after a workout aids in the recovery process by replenishing glycogen stores and facilitating muscle repair;
- Hydration and electrolyte balance: carbohydrates help maintain hydration levels by promoting water retention and electrolyte balance, which is essential during prolonged physical activities.
For those engaged in regular physical activity, the strategic intake of carbohydrates can significantly enhance both performance and recovery.
Mental health
The connection between carbohydrates and mental health is profound. Carbohydrates influence mood and mental clarity by regulating the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness.
- Mood regulation: a carbohydrate-rich diet can help stabilize mood swings and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety;
- Cognitive function: adequate carbohydrate intake ensures a steady supply of glucose to the brain, improving focus, memory, and cognitive function;
- Stress reduction: carbohydrates can also reduce stress levels by lowering cortisol, a stress hormone that can have detrimental effects when elevated.
Incorporating carbohydrates into our diet can thus play a vital role in maintaining mental health and enhancing overall quality of life.
Recommended daily intake: how much carbohydrate do we need?
Determining the right amount of carbohydrates to consume can depend on various factors, including age, gender, activity level, and overall health goals. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that 45-65% of daily caloric intake should come from carbohydrates.
Factors influencing carbohydrate needs:
- Age: younger individuals may require more carbohydrates to support growth and development;
- Activity level: highly active individuals or athletes often need a higher carbohydrate intake to fuel their energy expenditure;
- Health goals: those looking to lose weight might consume fewer carbohydrates, while those aiming to gain muscle mass might need more.
Healthy sources of carbohydrates
Choosing the right sources of carbohydrates is essential for maximizing their health benefits. Here are some nutrient-dense options:
- Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa and oats offer fiber and essential nutrients;
- Fruits: apples, bananas and berries provide natural sugars and vitamins;
- Vegetables: sweet potatoes, corn and carrots are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates;
- Legumes: beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in protein and fiber.
Incorporating a variety of these foods can ensure a balanced intake of carbohydrates, promoting both health and vitality.
Carbohydrates are undeniably essential for optimal health. From fueling our bodies with energy to supporting mental and physical well-being, their benefits are vast. By understanding the different types of carbohydrates and incorporating healthy sources into our diets, we can unlock their full potential.
In our journey towards health and wellness, let’s not shy away from carbohydrates but embrace them as an integral part of our balanced diet. Whether you’re an athlete aiming for peak performance or someone seeking mental clarity and vitality, carbohydrates can be your ally.